TRANSPORT LAYER
Allows traffic to be directed to specific network applications.Multiplexing:Transport layer gathers chunks of data it receives from different sockets and encapsulate them with transport headers. Passing these resulting segments to the network layer is called multiplexing.
Demultiplexing: The reverse process which is delivering data to the correct socket by the transport layer.
Port : Is a 16 bit number number that is used to direct traffic to specific services running on a networked computer.
ip:port number : Socket address
FTP - file tranfer . port 21
Ports with numbers 0–1023 are called system or well-known ports;
ports with numbers 1024-49151 are called user or registered ports, and
ports with numbers 49152-65535 are called dynamic and/or private ports.
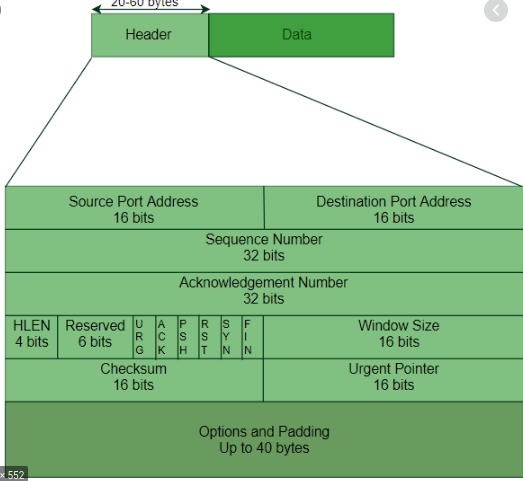
TCP SEGMENT :
Made up of TCP header and Data segment