DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolSubnet mask, Gateway, Name Server are same for all devices in the connected network.
Only IP addresses change.
• DHCP is an application layer protocol that automatesthe configuration process of hosts on a network.
DHCP DYNAMIC ALLOCATION:Most Common.
A range of IP addresses is set aside for client devices and one of these IPs is issued to these devices when they request.
AUTOMATIC ALLOCATION. —The DHCP server assigns a permanent IP address to a client from its.
FIXED ALLOCATION : requires a manually specified list of MAC address and their corresponding IPs
DHCP can be used for even NTP servers. Network Time Protocol servers: Used to keep all computers on a network synchronized in time.
DHCP DISCOVERY : The process by which a client configured to use DHCP attempts to get network configuration information.
1.DHCP DISCOVER : requests for network configuration info
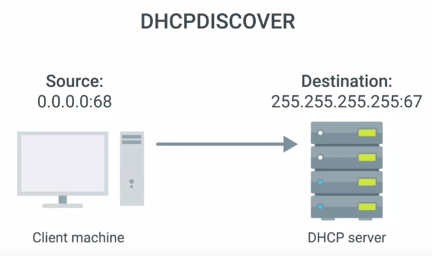
2. DHCP OFFER : Examines and offers to give it an IP
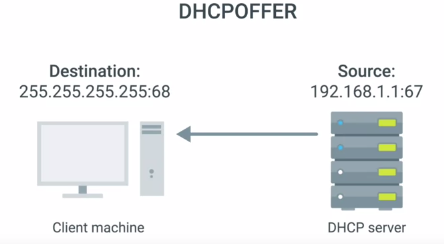
3. DHCP REQUEST : Local machine requests for an IP
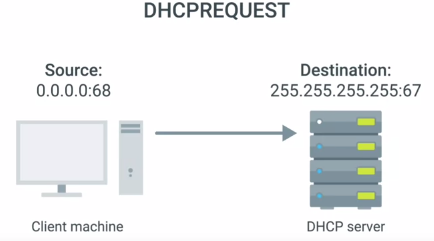
4. DHCP ACK :acknowledgement
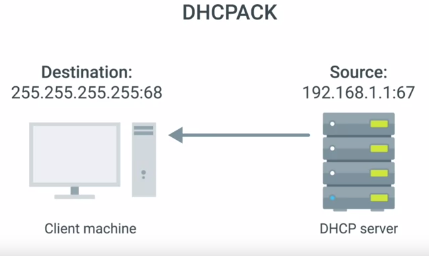
5. DHCP lease : includes an expiration