IP
IP addresses : 32 bit long numbersIP addresses belong to the network
Dynamic Host Configuration protocol : resolves ip dynamically
Dynamic IP address : clients
Static IP address : Network devices / servers
IP datagram : A highly structuredseries of firlds that are strictly defined.
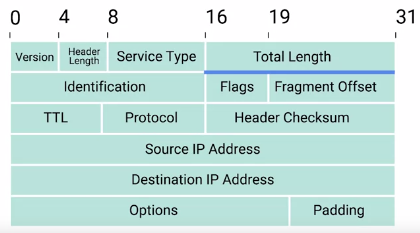
https://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=29578&seqNum=5
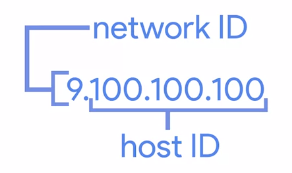
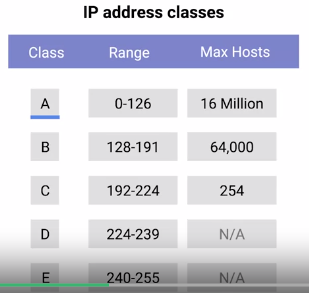
Address Class System : A way of defining how the global IP address space is split up.
1. Class A : First octet for network id ,rest for host id
2. Class B : First two octet for network id ,rest for host id
3. Class C : First three octet for network id ,rest for host id
CIDR : Classless inter-domain routing ...newly coming up
Address Resolution Protocol: A protocol used to discover the hardware address of a node with a certain IP address.
ARP table --→ A list of IP addresses and MAC addresses associated with devices